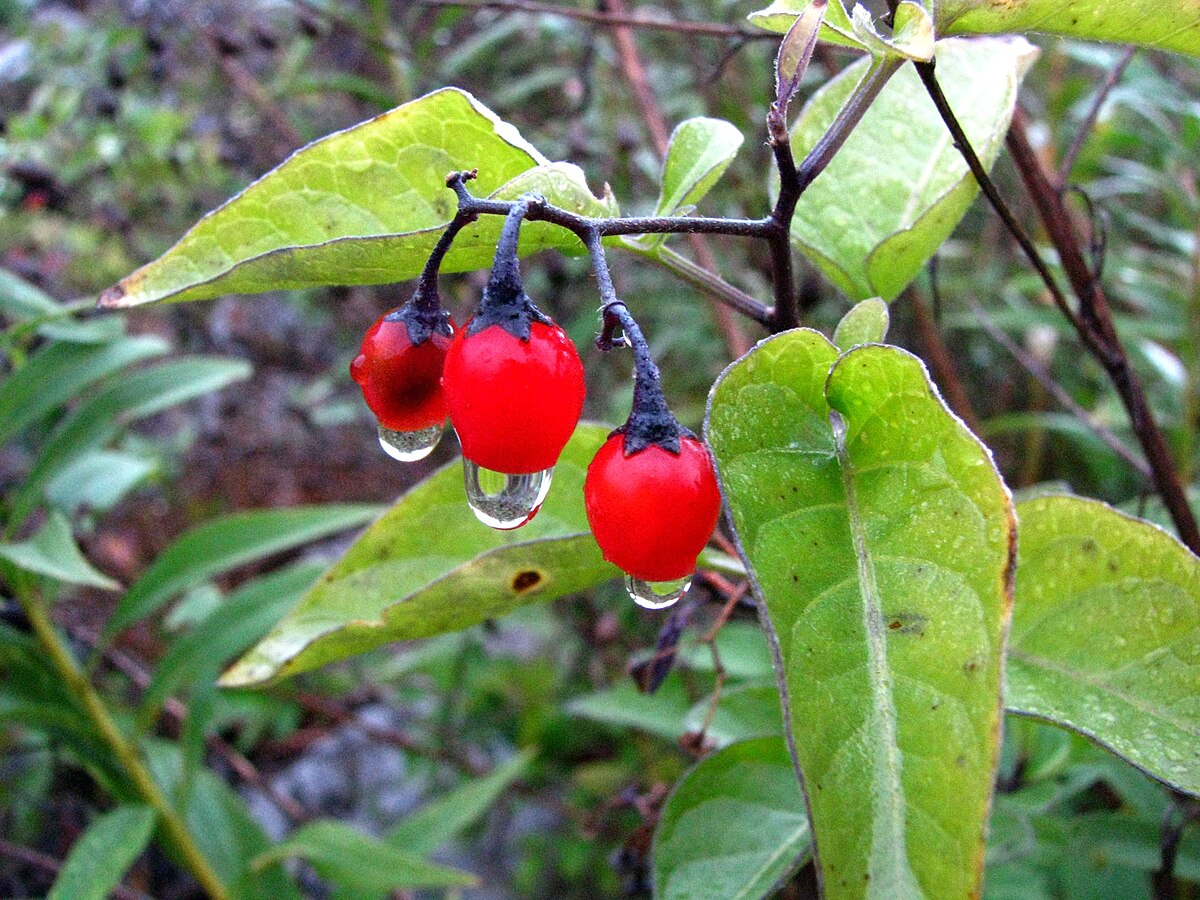
Solanum dulcamara L. – commonly known as Bittersweet Nightshade or Woody Nightshade – is a perennial vine native to Europe and Asia, now widely naturalized in North America. It thrives in moist, disturbed habitats such as woodlands, marshes, and hedgerows.
Botanical Profile
-
Family: Solanaceae (Nightshade family)
-
Parts Used: Twigs, root bark
-
Habitat: Moist woodlands, marshes, hedgerows
-
Plant Description: A perennial vine with trailing, slender stems that become woody with age. It produces purple, star-shaped flowers and red, berry-like fruits. The plant's distinctive appearance includes heart-shaped leaves and drooping flower clusters.
Chemical Constituents
Solanum dulcamara contains several bioactive compounds:
-
Alkaloids: Solanine (present in unripe fruits), solasodine (from flowers), and β-solamarine (from roots) .
-
Glycosides: Dulcamarin, contributing to its characteristic bitter taste .
-
Phenolic Compounds: Includes caffeic and ferulic acids, known for their antioxidant properties .
-
Flavonoids: Such as rutin and quercetin, which have anti-inflammatory effects .
Medicinal Uses
Historically, Solanum dulcamara has been utilized in traditional medicine, primarily for external applications:
-
Skin Conditions: Used in poultices for treating warts, ringworm, shingles, and old ulcers .
-
Respiratory Issues: The stem has been employed in treating bronchitis, asthma, and pneumonia .
-
Anti-inflammatory Effects: Some studies suggest potential benefits in reducing inflammation and treating conditions like psoriasis and eczema.
Note: The berries and leaves are toxic and should not be consumed. Only the stems, prepared correctly, have been used medicinally.
Safety and Precautions
Due to the presence of toxic compounds, especially in the berries and leaves, Solanum dulcamara should be used with caution:
-
Toxicity: The plant contains solanine, which can cause nausea, vomiting, and neurological symptoms if ingested .
-
Allergic Reactions: Some individuals may experience skin irritation or allergic reactions.
-
Medical Supervision: Always consult with a healthcare professional before using this plant for medicinal purposes.
Cultivation and Habitat
Solanum dulcamara is adaptable to various environments:
-
Growth Habit: Prefers moist, well-drained soils and can be found in woodlands, marshes, and along riverbanks.
-
Invasiveness: In some regions, it is considered an invasive species due to its rapid growth and spread.
Speech Disorder
A speech disorder, also known as a speech impairment...
ADHD
Attention-deficit / hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a...
Cerebral Palsy(CP)
Cerebral palsy (CP) is a group of neurological disorders...
Cancer
Cancer is a broad term for diseases where cells...