Family: Salicaceae (Willow Family)
Genus: Populus
Species: tremuloides
Common Names: Trembling Aspen, Quaking Aspen, White Poplar, Mountain Aspen
Parts Used:
-
Bark
Habitat & Distribution:
Populus tremuloides thrives in cooler regions of North America, often found in high mountain meadows of Baja California, the Juarez or Pedro Martir ranges, and throughout the United States. Interestingly, this species does not naturally occur in the Sierra region. It prefers moist, well-drained soils and is often seen forming extensive clonal groves through root propagation.
Plant Description:
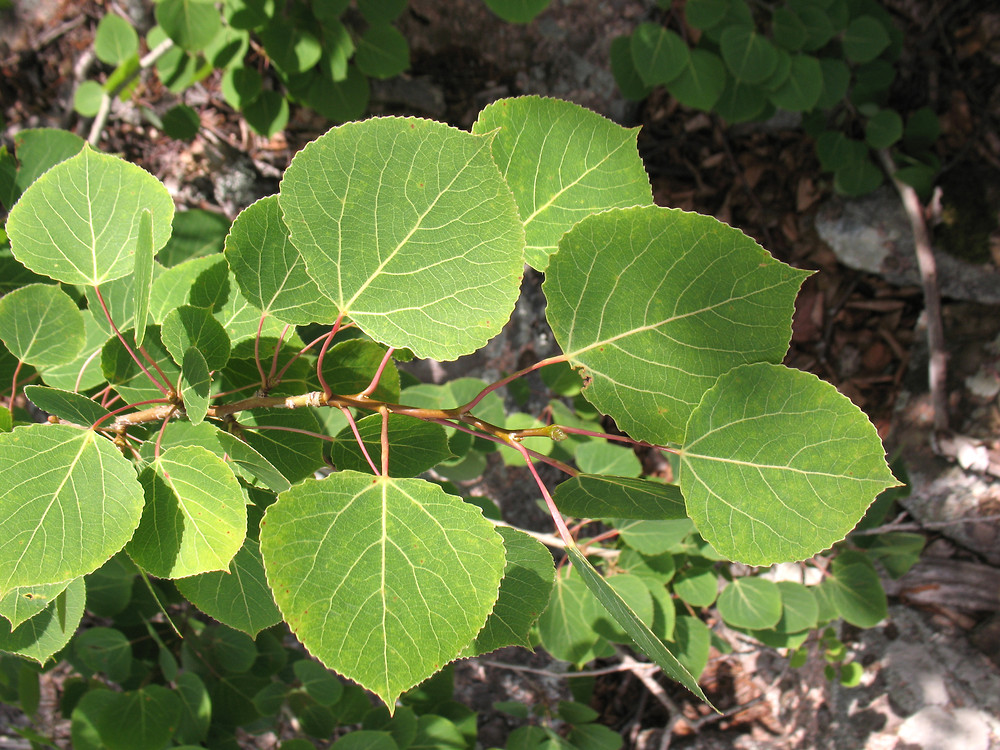
Populus tremuloides is a deciduous tree typically growing 15–25 metres (45–80 feet) tall. It’s known for its smooth, pale bark marked with black scars and its distinctive leaves that tremble in the breeze due to their flattened petioles — giving it names like Trembling Aspen and Quaking Aspen.
-
Leaves: Alternate, simple, heart-shaped to round, 1–3 inches long, deep green above and lighter beneath, with fine-toothed margins. In autumn, leaves turn a brilliant golden-yellow, occasionally with red hues.
-
Flowers: Dioecious (separate male and female trees). Both produce catkins 1–3 inches long, appearing between April and June.
-
Fruit: Light green capsules, 2–4 inches long, borne on catkins. Each capsule holds numerous small, hairy seeds.
-
Twigs: Slender, reddish-brown with a grayish waxy coating; conical, reddish-brown buds.
-
Bark: Initially smooth and creamy yellowish-white to light green, later becoming deeply furrowed and darkened near the base.
Medicinal Uses:
Traditional Uses:
-
Tea from the leaves or bark was traditionally taken to reduce fevers, relieve rheumatism, ease arterial swellings, and treat various skin conditions like eczema, wounds, burns, and gangrenous sores.
-
Topical washes made from the bark were applied to cuts, sores, and inflamed limbs.
-
The inner bark contains astringents like salicin and populin, known for drawing wounds together and promoting faster healing — a natural remedy resembling the effects of quinine.
-
Steeped root teas were traditionally given to expectant mothers nearing childbirth to prevent excessive bleeding and reduce the risk of premature labor.
-
Some records also note its use in alleviating body odour and addressing cancerous sores.
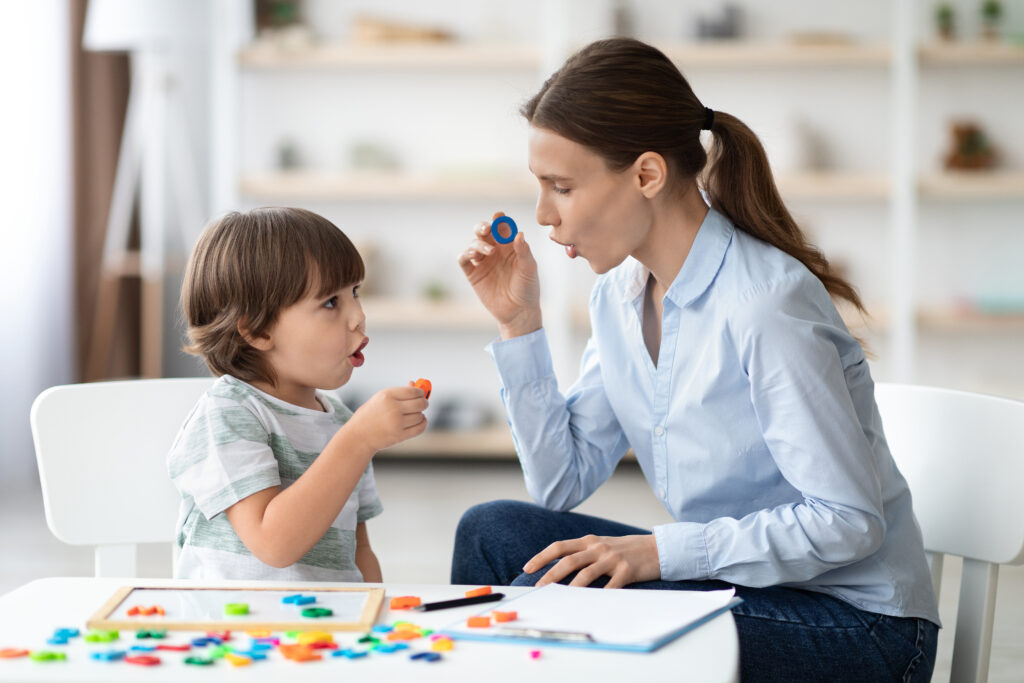
Speech Disorder
A speech disorder, also known as a speech impairment...
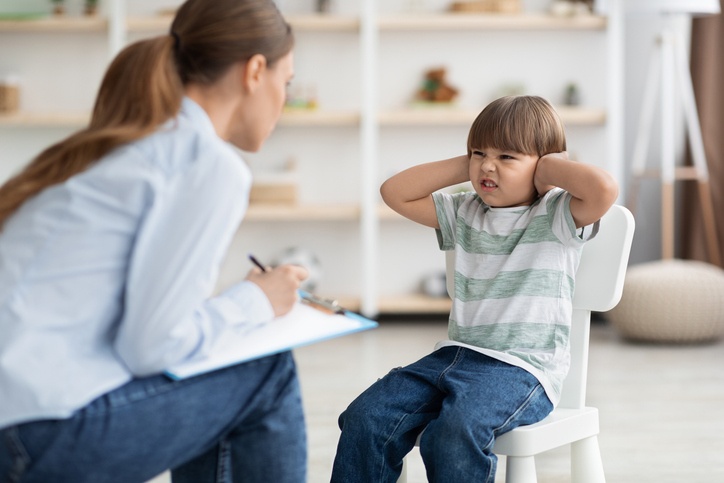
ADHD
Attention-deficit / hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a...
Cerebral Palsy(CP)
Cerebral palsy (CP) is a group of neurological disorders...
Cancer
Cancer is a broad term for diseases where cells...